Selecting insurance in Germany requires thoughtful evaluation of your needs, financial situation, and long-term plans. The system is structured around two main options: public and private insurance, each offering unique benefits, costs, and coverage levels.
Public insurance emphasizes accessibility and affordability, making it suitable for families and those with steady, moderate incomes.
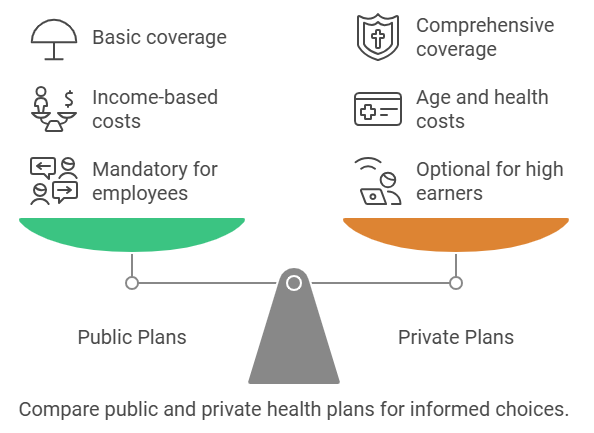
Key Points:
- Public plans are mandatory for most employees below a certain income threshold.
- Private options are available for high earners and self-employed individuals.
- Costs for public plans depend on income; private costs vary by age and health.
- Coverage in private plans can be more comprehensive but comes at a higher cost.
- Switching between the two can be challenging depending on circumstances.
What Is Public Health Insurance?
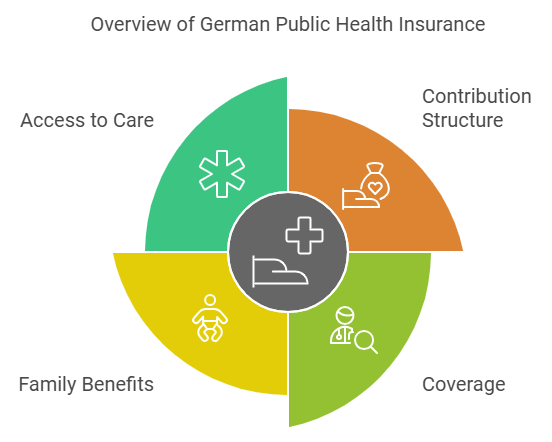
Contributions are income-based and deducted directly from salaries. This ensures affordability but may limit access to private-grade care.
Key Features of Public Plans
Public plans emphasize broad coverage. They include general medical services, prescriptions, hospital stays, and preventative care.
Dependents can often be included at no extra cost, which makes public plans appealing for families.
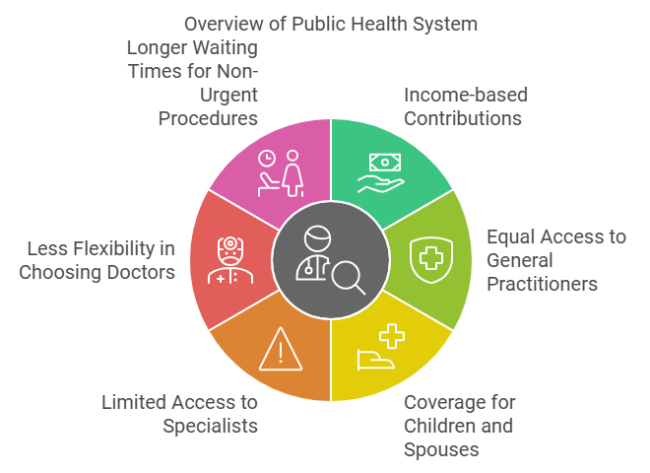
Public Health System Advantages:
- Income-based contributions.
- Equal access to general practitioners.
- Coverage for children and spouses.
- Public Plan Drawbacks:
- Limited access to specialists.
- Less flexibility in choosing doctors.
- Longer waiting times for non-urgent procedures.
What Is Private Health Insurance?
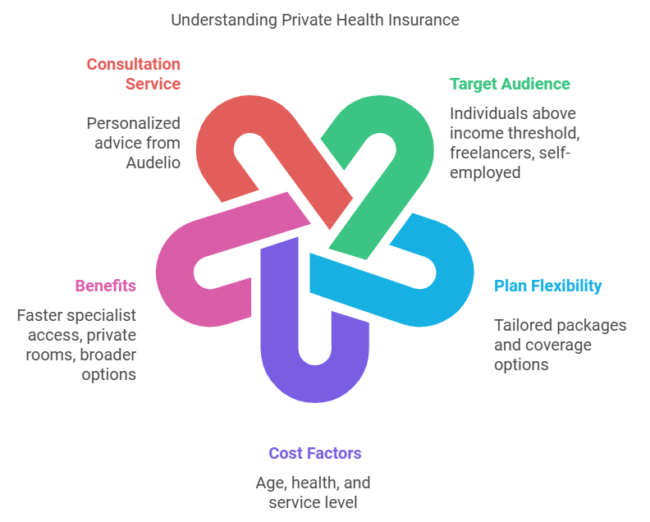
Private health insurance, caters to individuals above the income threshold, freelancers, and self-employed workers. Private plans come with flexibility in coverage and allow tailored packages. Costs depend on age, personal health, and the level of services chosen.
While premiums can increase with age, these plans often include benefits like faster access to specialists, private rooms during hospital stays, and broader treatment options.
For personalized advice on choosing the right plan, it’s worth consulting with Audelio. Audelio analyzes the entire insurance market with your interests at the center.
Key Features of Private Plans
Sieh dir diesen Beitrag auf Instagram an
Private insurance offers personalized coverage that adjusts to individual needs. While more expensive, it provides peace of mind with premium services.
Those eligible often value the ability to customize their health care experience.
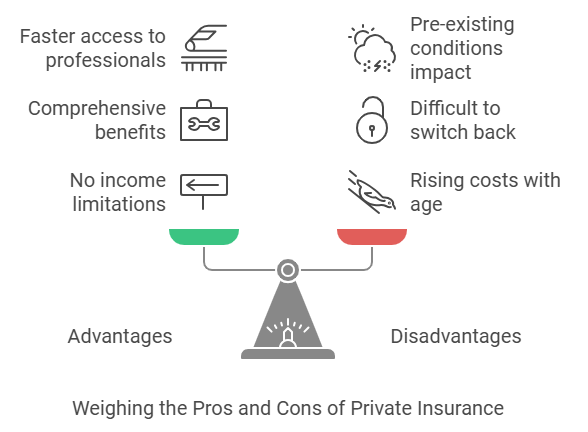
Advantages:
- No income-based limitations.
- Comprehensive benefits like dental and optical care.
- Faster access to medical professionals.
Disadvantages:
- Costs rise with age.
- Difficult to switch back to public insurance.
- Pre-existing conditions may affect coverage eligibility.
Supplementary Private Insurance for Public Plan Holders
Many public plan holders find supplementary coverage helpful for improving overall healthcare quality. It’s particularly valuable for those who anticipate needing specialized treatments or wish to reduce waiting times for specific services.
Which Option is Better for Expats?
Private insurance, on the other hand, can appeal to expats earning above the income threshold or seeking broader coverage. However, it requires careful planning, as it may be difficult to switch back to public insurance if long-term plans in Germany change.
Can You Switch Between the Two?
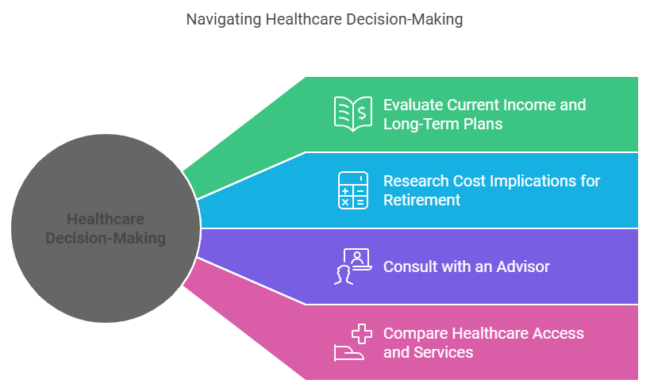
Important Steps to Consider:
- Evaluate current income and long-term plans.
- Research the cost implications for retirement.
- Consult with an advisor before making the decision.
- Comparing Healthcare Access and Services
Access to healthcare and the level of services differ significantly between public and private insurance.
However, non-urgent appointments often come with longer waiting times, especially for specialized care.
Costs and Contributions
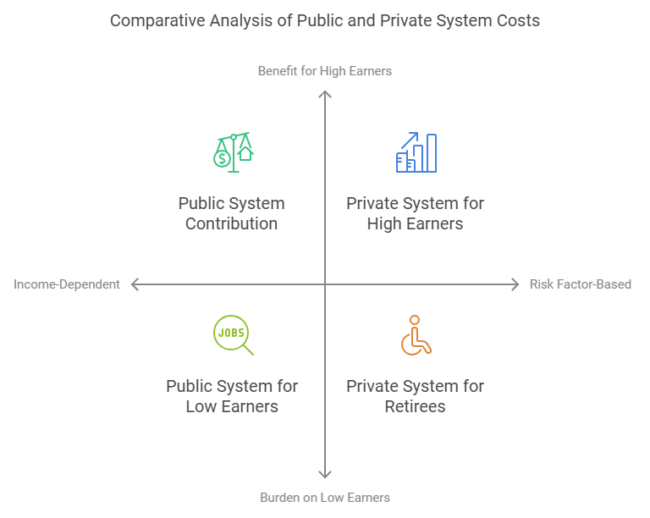
Public System Costs:
Employees contribute about 14.6% of their gross salary, shared equally with employers. Additional contributions may apply based on individual circumstances.
Private System Costs:
Premiums are calculated based on risk factors like age, health, and desired coverage. Unlike public contributions, costs are not income-dependent, which benefits high earners but may burden retirees.
FAQs
Conclusion
Choosing between public and private insurance in Germany depends on your income, profession, and health needs. Public options are generally better for families and those with stable, moderate incomes.
Private plans suit high earners or individuals prioritizing premium care. Understanding your unique circumstances and consulting experts can make the decision more straightforward.
