Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of children and adolescents worldwide. A deficiency causes by the hormone insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. Without proper management, diabetes can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. However, with reasonable care, children and adolescents with diabetes can lead healthy and active lives.
Managing diabetes in children and adolescents can be challenging, but it is essential for maintaining their overall health and well-being. The first step in managing diabetes is to work with a healthcare team that includes a pediatrician, diabetes educator, children’s Psychologist, and dietitian. This team will help create an individualized plan to manage your child’s diabetes that considers their age, growth and development, and activity level.
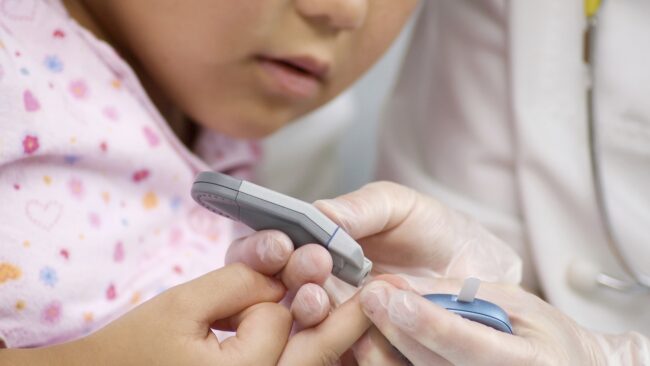
One of the most critical aspects of diabetes management is monitoring blood sugar levels. This can be done by using a glucose meter and testing strips, which measure the amount of glucose in the blood. It is important to check blood sugar levels at regular intervals, such as before meals and bedtime, to ensure they are within the target range.
Diet and physical activity are also crucial for managing diabetes in children and adolescents. A healthy diet should include a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats and be tailored to meet your child’s needs. Physical activity can also help control blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
Medications like insulin may also be necessary to manage diabetes in children and adolescents. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy, and it can be administered through injections or an insulin pump. Working with a healthcare provider to find the right type and dosage of insulin for your child is important.
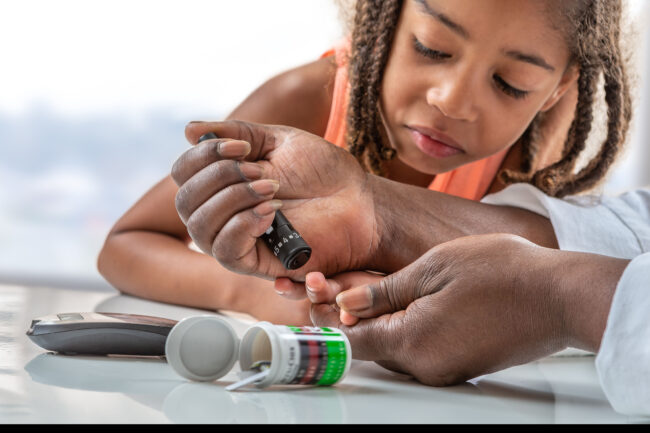
In addition to managing diabetes, it is also essential to teach children and adolescents the skills they need to manage their condition. This includes teaching them how to check their blood sugar levels, administer insulin injections or insulin pumps, and make healthy food choices.
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but with proper management, children, and adolescents can lead healthy and active lives. It is important to work with a healthcare team, monitor blood sugar levels, follow a nutritious diet, and engage in regular physical activity. By teaching children and adolescents the skills they need to manage their own diabetes, they can take control of their health and live fulfilling lives.
Children and adolescents with diabetes can have healthy, fulfilling lives with the proper support and care. The management of diabetes in children and adolescents necessitates collaboration between parents, medical professionals, and the child or adolescent themself. It is crucial to follow a personalized management plan, monitor blood sugar levels, maintain a nutritious diet, exercise regularly, and take medication as needed.

Educating parents and other adults responsible for children with diabetes about the warning signs and symptoms of high and low blood sugar levels is also crucial. Increased thirst, exhaustion, and frequent urination are all signs of hyperglycemia, commonly known as high blood sugar. Shakiness, disorientation, and sweat are hypoglycemia or low blood sugar signs. Parents and caregivers can take action by recognizing these symptoms.
Diabetes is a lifelong condition and children and adolescents must have the support they need to manage it successfully. Teaching children and adolescents the skills they need to manage their diabetes is key. This includes teaching them how to check their blood sugar levels, administer insulin injections or insulin pumps, and make healthy food choices.
It is also essential to empower them to take control of their diabetes by offering them choices about their diabetes care and helping them to set their own goals.
Supporting children and adolescents with diabetes also involves helping them to develop skills that will support them in managing their condition. These skills include problem-solving, communication, and decision-making. Encouraging children and adolescents to take part in activities that they enjoy and helping them to build a network of supportive friends can also help them to cope with their diabetes and build resilience.

Many children and adolescents with diabetes can benefit from psychological support. Having diabetes can be emotionally challenging, especially for younger children. It is important to provide children and adolescents with the opportunity to talk about their feelings and concerns about their diabetes.
A psychologist or psychotherapist can help children and adolescents to develop strategies for managing their stress, anxiety, and depression associated with diabetes. Family support is also an important factor in the successful management of diabetes.
The family needs to come together and agree on a plan of care that includes monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, and engaging in physical activity. Having a family member or friend with diabetes can be a difficult experience.

The healthcare team’s regular checkups are essential for managing diabetes. Children and teenagers with diabetes should schedule routine checkups to check their blood sugar levels, overall health, and growth and development. To ensure the diabetes management plan serves the child’s needs, it’s also crucial to review it routinely and make necessary adjustments.
Having a strategy in place in case of an emergency is also essential. Children with diabetes should always wear a medical identity bracelet or card that lists their emergency contact information and mentions that they have diabetes.
They should also always keep a glucose meter and a source of glucose, like glucose tablets, on hand. Additionally, parents and other caregivers should be able to spot hypoglycemia and hyperglycemic events and know how to react to them.

In summary, managing diabetes in kids and teenagers calls for a multifaceted strategy that includes keeping an eye on blood sugar levels, adhering to a balanced diet, regular exercise, and using medication when necessary.
To support the management of the child, parents, and caregivers must be knowledgeable about the warning signs and symptoms of high and low blood sugar, have an emergency plan, and schedule regular check-ups with the medical staff. Children and adolescents with diabetes can have healthy, fulfilling lives with the proper support and care.
