Accidents and emergencies can happen when we least expect them, often in places where immediate medical help is not available. Knowing how to perform CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) and first aid can make the difference between life and death. Being equipped with these essential skills allows you to act confidently and effectively in critical situations.
Understanding CPR and Its Importance
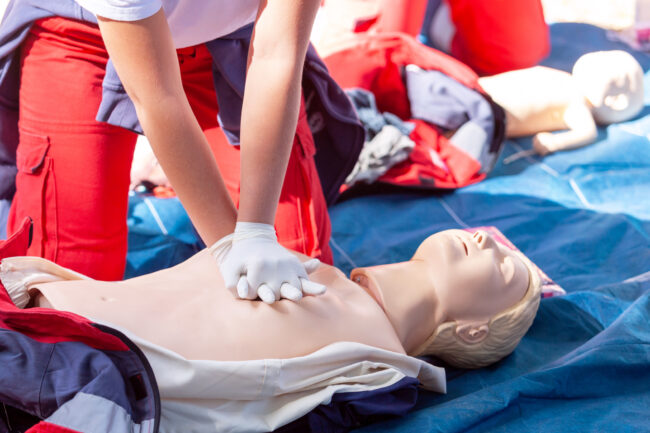
CPR is a lifesaving technique used in emergencies when someone’s heartbeat or breathing has stopped. This might occur due to a heart attack, drowning, electric shock, or other life-threatening situations. The primary goal of CPR is to maintain blood flow to the brain and heart, delaying tissue death and extending the window of opportunity for successful resuscitation without permanent damage.
The main objectives of CPR are to restore circulation, ensure oxygenation, and keep the heart responsive. Restoring circulation is crucial because it manually pumps the heart to maintain blood flow to vital organs. Ensuring oxygenation helps supply oxygen to the brain, reducing the risk of brain damage. Keeping the heart responsive is important because effective CPR can keep the heart in a state that is more receptive to defibrillation, which is often necessary to restart a normal heart rhythm.
The Basic Steps of CPR
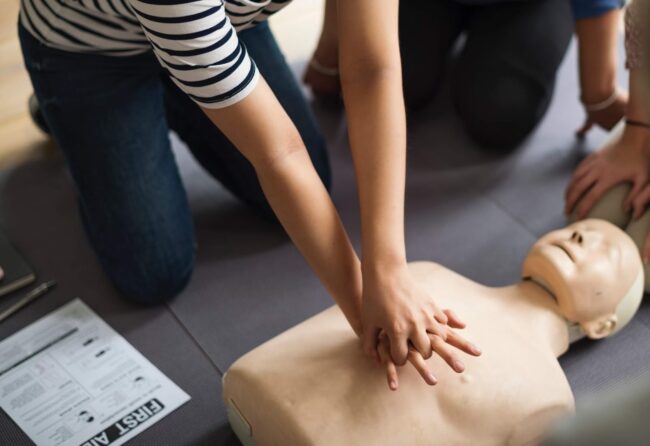

The CPR procedure involves a cycle of chest compressions and rescue breaths.
First, assess the situation to ensure it is safe for both the rescuer and the victim. Quickly check if the person is responsive by shouting and gently shaking their shoulders. If there is no response, call emergency services immediately. If others are nearby, instruct someone to call for help while you start CPR.
Next, check for breathing. Look for normal breathing patterns. If the person is not breathing or only gasping, you need to begin CPR immediately. Place your hands, one over the other, in the center of the chest and use your upper body weight to compress the chest about 2 inches deep at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. It is important to allow the chest to recoil completely between compressions to ensure effective blood flow.
After completing 30 chest compressions, open the airway by tilting the head back and lifting the chin. Pinch the nose shut, cover the person’s mouth with yours, and blow to make the chest rise. Give two rescue breaths, each lasting about one second. Continue this cycle of 30 compressions followed by two breaths until professional help arrives or the person begins to show signs of life, such as breathing or movement.
Knowing when to stop CPR is crucial. CPR should be continued until professional medical help arrives and takes over, the person shows signs of life, or you are too exhausted to continue. If you are the only rescuer and there are no signs of life after prolonged CPR efforts, it is advisable to continue until medical professionals arrive.
First Aid Techniques Everyone Should Know
Alongside CPR, basic first aid techniques can be crucial in stabilizing an individual until professional help is available. Here are some essential first aid measures to be familiar with:
- Treating Cuts and Wounds: To manage bleeding, apply direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or bandage. Elevate the injured area above the heart level if possible. If the bleeding is severe and does not stop, seek medical help immediately.
- Burns: For minor burns, cool the affected area under running cold water for at least 10 minutes. Avoid using ice directly on the burn, as this can cause further tissue damage. Cover the burn with a sterile, non-adhesive bandage or clean cloth. For severe burns or those involving large areas of the body, seek emergency medical help immediately.
- Choking: For an adult or child who is choking, perform the Heimlich maneuver. Stand behind the person, wrap your arms around their waist, and make a fist with one hand. Place the fist slightly above the navel and grasp it with your other hand. Quickly thrust inward and upward to help dislodge the object from the airway. For infants, administer back blows and chest thrusts instead of the Heimlich maneuver.
- Sprains and Strains: Apply the R.I.C.E. method—Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Rest the injured area, apply ice to reduce swelling, use a compression bandage to support the injury, and elevate the affected limb to decrease swelling.
- Seizures: If someone is having a seizure, do not restrain them or place anything in their mouth. Clear the area around them to prevent injury and place a soft object under their head. Once the seizure stops, roll the person onto their side in the recovery position and stay with them until they regain full consciousness.
The Importance of First Aid and CPR Training
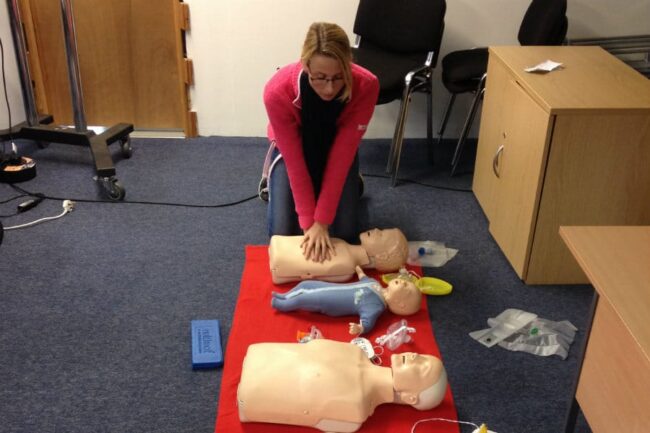
Learning CPR and first aid is not just about acquiring skills; it’s about being prepared to take action in emergencies. By having this knowledge, you can provide immediate assistance, potentially saving lives before emergency responders arrive. CPR training is widely available through various organizations, including online certification programs like MyCPR NOW, which offer comprehensive and convenient courses that fit into busy schedules.
First aid training equips individuals with the ability to recognize and respond to common injuries and medical emergencies. With proper training, individuals can perform life-saving measures confidently and effectively. For instance, being trained in first aid techniques can help in managing wounds, dealing with burns, or assisting someone choking. These skills are invaluable, not just in public spaces but also at home, where many accidents occur.
CPR and First Aid Techniques: A Quick Reference Table
The table below provides a quick reference for CPR and first aid techniques to remember in emergencies:
| Emergency Situation | Steps to Take |
| Unconscious, Not Breathing | Perform CPR: 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths |
| Severe Bleeding | Apply direct pressure, elevate the wound, seek medical help |
| Burns | Cool with running water, cover with a clean cloth, seek help for severe burns |
| Choking | Perform Heimlich maneuver for adults/children; back blows and chest thrusts for infants |
| Sprains/Strains | Use R.I.C.E: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation |
| Seizures | Clear the area, place a soft object under head, turn on side post-seizure |
Conclusion
CPR and first aid are critical skills that everyone should learn. Knowing how to respond in emergencies can save lives and prevent injuries from becoming more severe. By equipping yourself with these essential techniques, you become a valuable resource in your community, capable of stepping up when it matters most.
