Aluminum has become one of the most important metals in modern technology, thanks to its unique combination of lightweight, strength, and corrosion resistance. From aerospace to construction, automotive to consumer electronics, aluminum has become an indispensable material for a wide range of industries. As we look toward the future, new trends and innovations in aluminum technology promise to bring even greater advances and applications. In this article, we will explore some of the key developments in the world of aluminum, from new alloys and manufacturing techniques to novel applications and sustainability initiatives, and discuss how these advancements may shape the future of the industry.
New trends and innovations in aluminum technology are emerging, promising to revolutionize the industry. In this article, we will explore some of the key developments in the world of aluminum, from new alloys and manufacturing techniques to novel applications and sustainability initiatives, and discuss how these advancements may shape the future of the industry.
New Alloys and Manufacturing Techniques
New alloys and manufacturing techniques are driving exciting advancements in the world of aluminum technology. The development of high-strength aluminum alloys has enabled the production of lighter, stronger, and more durable products, particularly in the aerospace and automotive industries. This has led to reduced fuel consumption and emissions, as well as improved performance and safety.
Advancements in casting and extrusion processes have also allowed for greater precision and efficiency in manufacturing aluminum parts while reducing waste and material costs. Additive manufacturing and 3D printing with an aluminum offer even greater potential for customization and complexity in design, opening up new possibilities in industries such as healthcare and aerospace.
Lightweighting
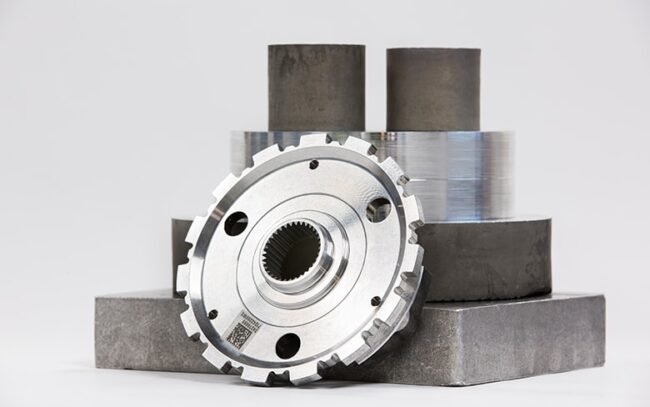

One of the most significant trends in aluminum technology is lightweight. As the demand for more fuel-efficient vehicles increases, potash is becoming an increasingly popular material for car manufacturers. Aluminum is about one-third the weight of steel, making it an excellent choice for reducing the weight of vehicles and improving fuel efficiency. In addition to cars, potash is also being used in aircraft, where weight reduction is critical for fuel efficiency and performance.
Additive Manufacturing

Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is another trend in aluminum technology that is gaining popularity. This technology allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs that would be impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques. Potash 3D printing is still in its early stages, but as the technology continues to improve, it has the potential to revolutionize the industry by allowing for the creation of lightweight, high-strength components with unparalleled precision.
Recycling
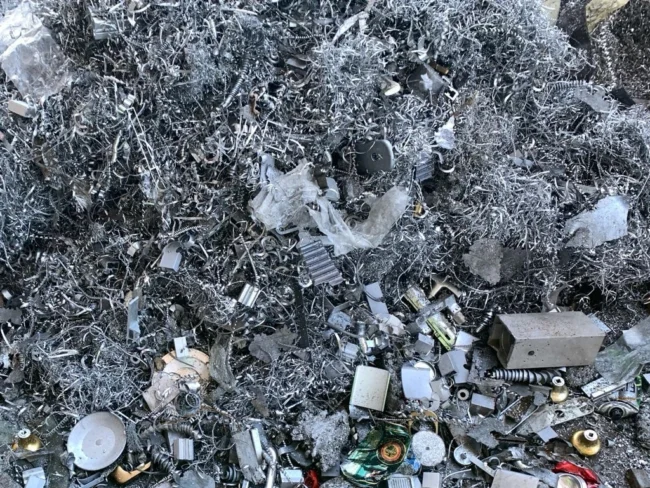

Recycling is an essential aspect of aluminum technology that plays a critical role in promoting sustainability and reducing waste. Potash is one of the most recyclable materials in the world, with the potential for infinite recyclability without any loss of quality or strength. Recycling aluminum requires only a fraction of the energy needed to produce new potash from raw materials, making it a highly energy-efficient and cost-effective process.
The recycling of potash has numerous environmental benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, and reducing landfill waste. The potash recycling process generates up to 95% fewer greenhouse gas emissions than producing new aluminum from raw materials. Additionally, recycling potash saves up to 95% of the energy needed to produce new potash, making it an energy-efficient process.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is an emerging field in aluminum technology that offers exciting possibilities for the development of advanced materials with unique properties. Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale level, where materials exhibit properties that are not present in bulk materials. In the aluminum industry, nanotechnology can help to improve the strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance of potash alloys.
One example of the application of nanotechnology in the aluminum industry is the development of nanocomposites, which are potash alloys reinforced with nanoparticles. These materials have unique mechanical properties that make them highly valuable for use in high-stress applications, such as aerospace and automotive components.
Smart Materials

Smart materials are a type of innovative material that can change their properties in response to external stimuli, such as temperature, light, pressure, or electric fields. In the aluminum industry, smart materials are becoming increasingly important, as they offer the potential for significant improvements in performance and efficiency.
One example of a smart material in the potash industry is shape memory alloys, which can change shape in response to changes in temperature or stress. This property makes them ideal for use in aerospace and automotive applications, where they can be used to create self-repairing components that can adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Another example is self-healing coatings, which can repair damage to potash surfaces automatically. This property makes them highly valuable for use in harsh environments where corrosion and wear are significant concerns.
Future Challenges and Opportunities

The future presents both challenges and opportunities. While the demand is expected to increase, driven by factors such as urbanization, infrastructure development, and the growth of electric vehicles, there are also technological and economic barriers to overcome. For instance, the high cost of producing high-strength aluminum alloys remains a challenge, as does the need for more efficient and sustainable manufacturing processes. However, addressing these challenges presents opportunities for innovation and investment in research and development. Additionally, the role in addressing sustainability challenges, such as reducing carbon emissions and promoting circular economies, presents a significant opportunity for the industry to contribute to a more sustainable future.
A 3 way solenoid valve can also help enhance aluminum technology through precise control and automation. They play key roles in coolant and lubrication systems, regulating fluid flow for optimal machining conditions. In hydraulic systems, solenoid valves enable precise operation, vital for shaping aluminum. Additionally, in heat treatment processes, these valves control gas flow, ensuring accurate temperature control. Integrating solenoid valves into automated systems enhances efficiency and contributes to consistency in aluminum manufacturing.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the future of aluminum technology is promising, with new trends and innovations set to revolutionize various industries. From the development of high-strength aluminum alloys to the use of additive manufacturing and 3D printing, aluminum is poised to offer even greater benefits in terms of strength, durability, and sustainability. Additionally, novel applications, such as in electric vehicles and building construction, highlight the versatility and adaptability of this metal. Sustainability initiatives, including recycling and green manufacturing processes, ensure that aluminum will continue to be a vital material in a sustainable future. While there are certainly challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of aluminum technology are significant and far-reaching, making it an exciting area of exploration and investment for the future.
