If you’ve ever had the opportunity to unscrew some appliance, or at least watched someone else do it, we’re sure you’ve immediately noticed the board, most often green in color with a large number of tiny components connected to it.
If you are an amateur in this, this board will act like a real little chaos: from a bunch of miniature pieces of different shapes to intertwined wires of different colors. However, if you are a professional, then you know that it is all just not chaos and that each part has its place and function so that the device can work properly.
This board is very important in electronics and is professionally called printed circuit board or abbreviated PCB. The primary purpose of PCBs is to securely connect electronic parts in devices, whether we are talking about various consumer or non-consumer devices.
When it comes to PCBs, for many, the first association, perhaps the only one, will be rigid PCBs, most often greenish. However, in addition to rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs can also be found on the market. So when we talk about PCBs one does not always have to think of hard boards. Now you are probably wondering what are the basic differences between these two types of PCBs and which one is better to use. Find out more about all the details below.
Materials from which they are made
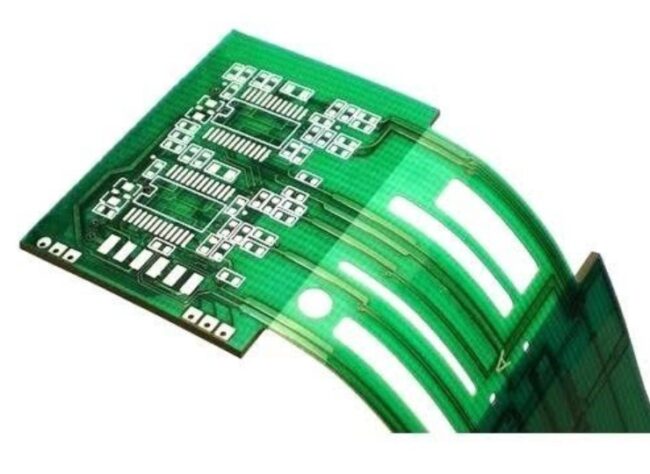

Although the function of both PCBs is identical, the first difference is in the material from which they are made. Rigid PCB is a fairly strong glass-reinforced substrate. It is this that gives it exceptional strength and rigidity. It is extremely safe and gives great support to the components on it. Also, the materials from which it is made are heat resistant.
Flex PBC, like rigid, has conductive tracks on a non-conductive substrate. The basic material from which they are made is polyimide. The flexibility of this PCB allows the components to better withstand vibration as well as heat. In terms of strength and quality, they are exactly the same in this sense as rigid PCBs.
Weight of these PCBs
The weight of these plates depends on their thickness and dimensions. However, let’s compare these two boards of almost the same dimensions, it is clear that rigid PCBs are a bit heavier than flexible ones. This is a consequence of their strength and thickness. This fact can be very useful when creating smaller devices that are expected to be as light as possible.
Heat resistance
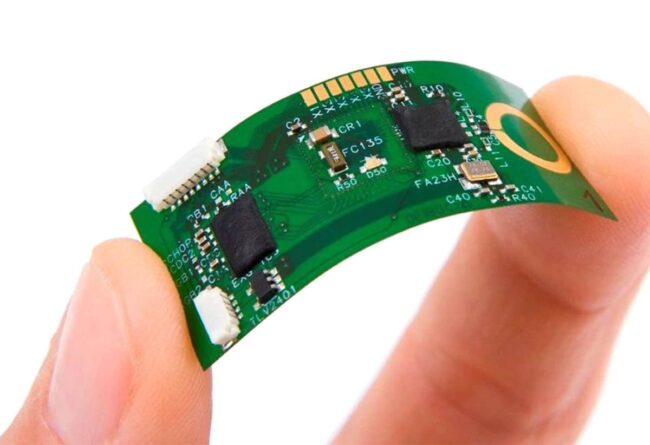
The heat generated in certain devices is very easily tolerated for both types of PCBs. However, if we are talking about extraordinary, extreme conditions where high temperatures occur, preference must be given to flex PCBs. They are much more resistant to high temperatures, unlike solid PCBs, which can damage or lose their shape.
Vibration transmission resistance
This is another field where the winner will be flex PCB. Since they are made of flexible material that can be bent and adjusted, it is clear that this PCB will be much better able to withstand shocks, drops or any other vibrations created by the device itself.
In this sense, a rigid PCB is quite rigid and again there is a possibility that it will wear out or be damaged by some runaway vibrations. That is why flex PCBs are most often used for portable devices.
Use value

We have already mentioned that both types of PCBs have the same function and therefore use-value. Rigid PCBs are more used for simpler devices used by consumers. For example, they are used for different types of keyboards, toys that have a certain voice or lighting capabilities, certain TV and radio devices, monitors, computers, and the like. In all of these products, the solid PCB is proven to work well.
When we talk about flex PCBs, you can see on pcbasic.com that they are more often used for very complex products. This type of PCB is found in very compact devices, ie in high-performance devices. Here we can count tablets, smartphones, GPS devices, cameras, and generally all portable devices. Flex PCB is also used when it comes to low technology. For example, an ice strip is placed on a flex PCB.
However, if the production of the device so requires, both rigid and flex PCBs can be used together. This would take advantage of the unity of their strengths and provide the maximum.
Production price
As for the cost of manufacturing these PCBs, usually flex PCBs cost a bit more than rigid ones. However, modern production is constantly facing new challenges in terms of reducing the size of its products, and flex PCB has grown up to such requirements. In this way, the price is fully justified.
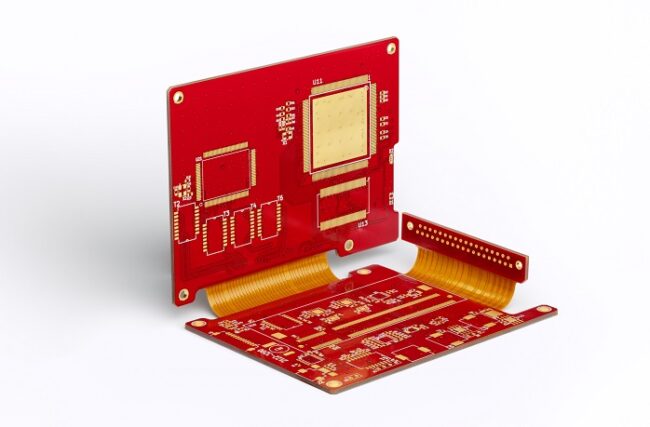
What are rigid-flex PCBs?
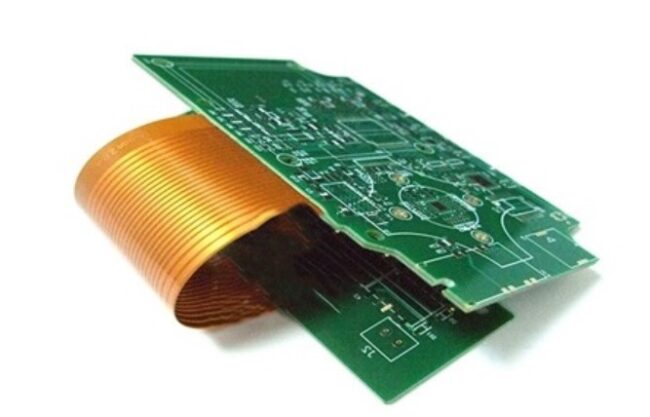
Rigid-flex PCBs are a combination of the best qualities of both rigid and flex PCBs. As a result of the sleep of these two types of PCBs, a very resistant PCB has been produced which has an extremely wide application in many industries.
This combination is much stronger, more stable, and versatile than both of these boards individually. It works great even in the most complex devices, they are safe, reliable, very lightweight and can be produced in very miniature sizes. In this way, they meet most of the manufacturer’s criteria, especially when it comes to saving space.
However, as you can guess, the price of these combined PCBs is much higher than both rigid and flex PCBs. However, wide use and high resistance justify the price.
Whether rigid PCCB or flex PCB, both boards have the same purpose, again, they connect various electrical and mechanical components. Rigid and flex PCBs are used almost equally in the production of devices and apparatus.
Both found their place and justified their existence. While some are accustomed to using rigid PCBs and their ease of use, flex PCBs still require adherence to certain rules and performance. Hope that this text has helped you understand the benefits of these two tools.
